In-depth Analysis: Supply Chain, Production Technologies (with Emphasis on Distillation), Trends and Challenges
This article gives a concise view of the global fatty acids sector (also called carboxylic acids or alkanoic acids), clarifying scope, size, and why it matters to buyers, producers, and investors.
Published estimates vary widely due to scope differences (coverage of derivatives, chain-length ranges, and inclusion of soap noodles or specialty esters). Recent sources place 2024–2025 market value in a band from roughly USD 22–33 billion, while some broad-scope reports cite over USD 100 billion when downstream derivatives are included. Typical reported CAGRs for 2025–2032 cluster around 4–6%.
Fatty acids are foundational to consumer staples (cleaning, personal care, food), to bio-based chemicals substitution, and to low-carbon supply chains. The industry’s shift to sustainable sourcing and energy-efficient separation is reshaping cost curves and risk profiles for global brands.
| Region | Role in Market |
|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific | Largest producer and consumer |
| Europe | Specialty grades, regulatory leadership |
| North America | Mature demand, innovation clusters |
| Latin America | Growing oleochemicals footprint |
| Middle East & Africa | Emerging consumption and logistics |
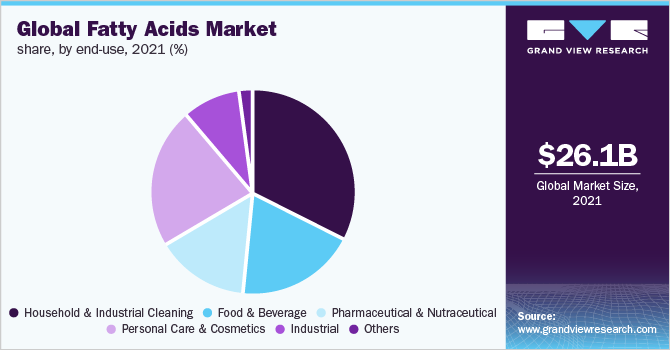
Global fatty acids end-use share snapshot, illustrating major demand segments in cleaning, food, pharma, personal care, and industrial applications.
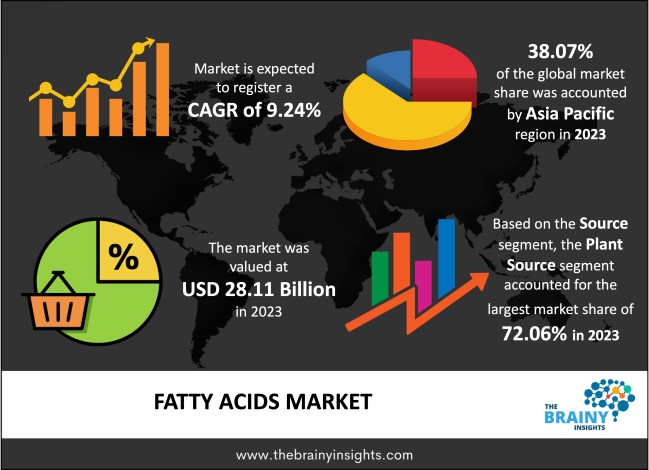
World map infographic showing regional growth dynamics and plant-based source prominence in the global fatty acids industry.
This section maps the fatty acids industry value chain end-to-end and pinpoints where value accrues and risks emerge.
This section explains the core production technologies, with a pragmatic focus on fractional distillation as the industry backbone.
Routine analytics: GC-FID carbon-number profiling, acid value, iodine value, saponification value, color, peroxide value, odor threshold.
Standards and certifications: USP/NF and FCC for food/pharma, Kosher/Halal where applicable, ISO 9001/14001, and RSPO/ISCC for sustainable supply claims.
| Method | Primary Purpose | Strengths | Constraints | Typical Use-Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrolysis | Split triglycerides | Mature, scalable, co-produces glycerin | Requires energy and high-pressure kit | Base step for most oleochemical plants |
| Fractional Distill. | Purify by carbon number | High purity, flexible, industry standard | Energy and capex intensive | All major single-cut fatty acid production |
| Short-path Distill. | Gentle finishing/deodorization | Low thermal stress, protects color | Lower throughput | Premium grades, heat-sensitive fractions |
| Hydrogenation | Saturation adjustment | Stability, custom melting profile | Catalyst handling, selectivity control | Stearic-rich or oxidative-stable grades |
| Enzymatic Processes | Selective, low-temp conversions | Selectivity, potential lower footprint | Cost, enzyme lifetime, scale-up | Specialty esters, gentle splitting niches |
Expect steady mid-single-digit growth, with outsized gains in home and personal care, nutraceuticals, and bio-lubricants. The winners will combine assured sustainable feedstock access, energy-efficient distillation, and tight quality systems, while de-risking logistics and carbon exposure.