GAA“Glacial Acrylic Acid”
Global Market Overview, Industry Chain Analysis
How to Obtain High-Quality GAAThis Global Market Overview and Industry Chain Analysis of Ice Crystallized Acrylic Acid covers core production technologies with emphasis on melt crystallization and a concise read on industry trends and challenges.
1. Executive Summary
Ice crystallized acrylic acid, commonly called glacial acrylic acid (also acide acrylique glacé, ácido acrílico glacial), is a high-purity monomer used in superabsorbent polymers (SAP), acrylate esters, coatings, and adhesives.
Market size signals are resilient. The glacial acrylic acid industry is projected to grow from USD 14.12 billion in 2025 to USD 19.01 billion by 2034 (CAGR ~3.4%) per Market Research Future. Broader acrylic acid volumes are expected to reach 8.18 million tons in 2025 and 10.52 million tons by 2030 (CAGR ~5.15%) according to Mordor Intelligence. MarketsandMarkets estimates the acrylic acid value pool at USD 11.3 billion in 2023, reaching USD 13.8 billion by 2028 (3.3% CAGR).
Industry chain snapshot: upstream propylene and catalysts; midstream propylene oxidation to acrylic acid and purification to glacial grade; downstream SAP, acrylates, coatings, and hygiene products.
Key technology highlight: melt crystallization delivers high-purity, energy-efficient, low-polymerization-risk purification versus deep-vacuum distillation.
Main trends: stable hygiene demand, Asia-Pacific capacity leadership, energy and carbon intensity pressure, and incremental upgrades to safer, lower-VOC production and logistics.
2. Market Overview
2.1 International Landscape
Terminology is consistent globally: glacial acrylic acid (GAA) or ice crystallized acrylic acid denotes ≥99.5% purity monomer that solidifies near ambient conditions (melting point ~13–14°C).
Segmentation by end use is dominated by SAP (diapers, adult incontinence, femcare), followed by acrylate esters (butyl/2-EH acrylate) for coatings and adhesives, and water treatment polymers.
Regional structure shows Asia-Pacific as the capacity and demand center, with Europe and the Americas as mature, technology-intensive markets. Indicative consumption shares and patterns:
| Region | Approx. Share | Primary Applications | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific | 45–50% | SAP, acrylates, adhesives | China leads capacity; intra-Asia trade strong |
| Europe | 20–25% | Coatings, hygiene, adhesives | High regulatory stringency; focus on energy efficiency |
| Americas | 20–25% | SAP, coatings, oilfield | Stable hygiene demand; specialty esters |
| MEA | 5–10% | Hygiene, construction | Import-reliant; gradual downstream build-out |
Supply-demand balance remains tight around maintenance seasons and propylene price spikes. Trade flows typically move from Asia and Europe to deficit regions in MEA and selected Latin American markets. Merchant GAA availability is sensitive to SAP plant turnarounds and inhibitor logistics.

Figure 1: Simplified melt crystallization process flow for ice crystallized acrylic acid, including coolers, crystallizers, wash columns, and melt circuits.
2.2 Demand and Sectors
- Hygiene leads global demand via SAP-grade monomer; demographics and premiumization support steady growth.
- Coatings and pressure-sensitive adhesives benefit from construction and packaging recovery.
- Water treatment and functional polymers add incremental volumes, while electronics and 3D printing resins emerge selectively.
- Regulatory drivers: low-VOC formulations, stricter monomer exposure limits, and growing customer preference for lower-carbon products.
3. Industry Chain
3.1 Upstream
- Feedstocks: polymer-grade propylene (from naphtha crackers or PDH), air/oxygen, and Mo-V based mixed oxide catalysts; inhibitors such as MEHQ/PTZ; utilities and nitrogen blanketing.
- Supply patterns: Asia adds PDH-linked propylene; Europe and the US balance cracker and PDH sourcing. Logistics include refrigerated/temperature-controlled tanks to manage GAA solidification and polymerization risk.
3.2 Midstream
- Two-step oxidation: propylene to acrolein, then to acrylic acid over fixed-bed catalysts.
- Primary recovery: absorption, dehydration, and crude acrylic acid stabilization with inhibitors.
- Purification to glacial grade: hybrid sequences using extraction/distillation and, increasingly, melt crystallization to reach ≥99.5% purity with low color and controlled inhibitor levels.
- Byproducts: acetic acid traces, maleic species, aldehydes; off-gas and wastewater minimization via heat integration and emission controls.
3.3 Downstream
- Derivatives: sodium polyacrylate SAP, butyl/2-ethylhexyl/methyl/ethyl acrylates via esterification, and water-soluble polymers.
- Distribution: ISO tanks, heated tank cars, and insulated drums; inhibitor and temperature control are critical for safety.
- End users: hygiene converters in APAC/EU/US; coating producers and adhesive formulators globally.
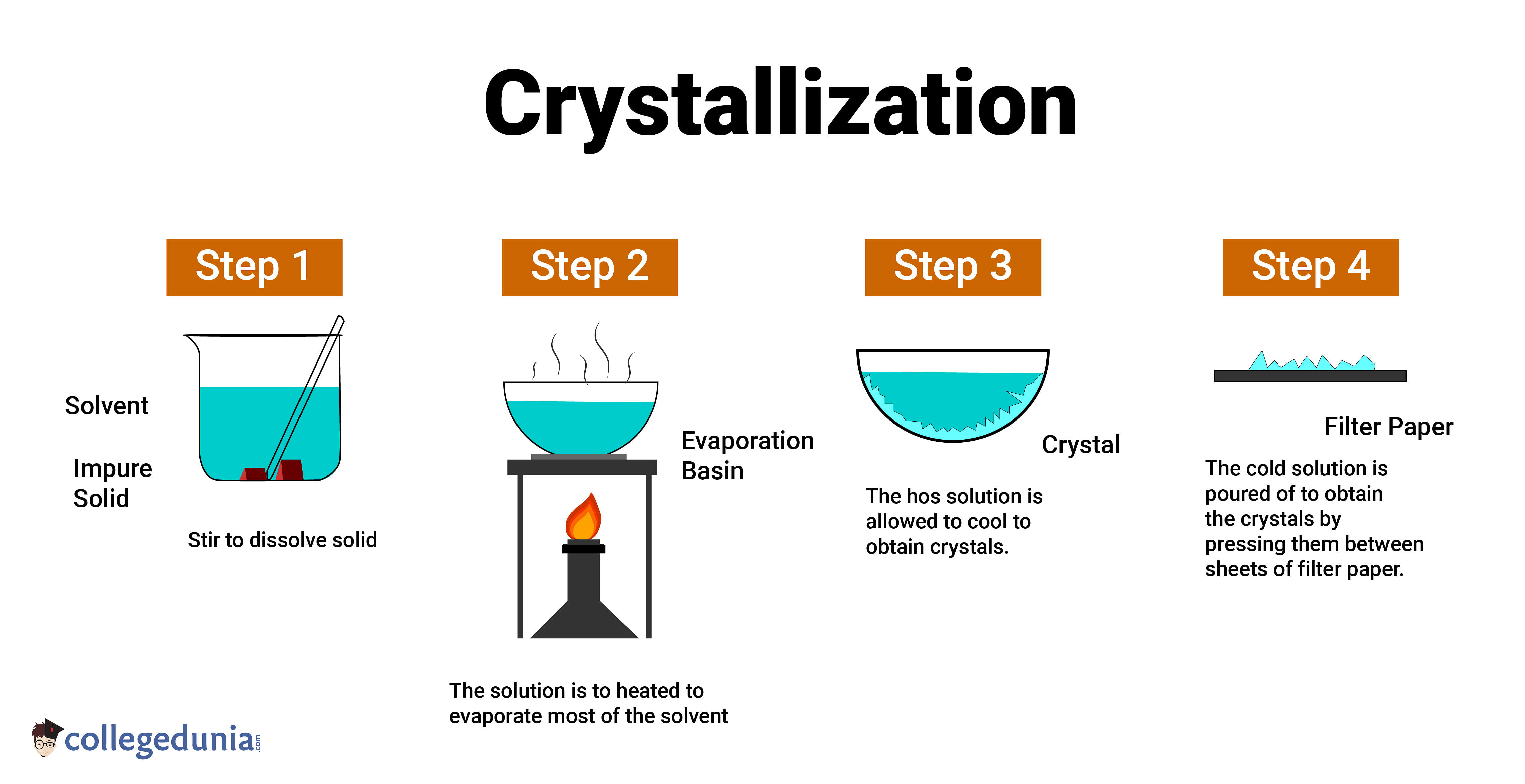
Figure 2: Generic crystallization steps from solution to crystal formation, illustrating cooling and filtration concepts relevant to melt crystallization design.
4. Core Technologies
4.1 Major Technologies
Glacial acrylic acid purification historically relied on multi-effect, deep-vacuum distillation and solvent extraction. These methods are effective but energy-intensive and can elevate polymerization risk at high temperatures.
Melt crystallization ( fusion cristallisation, cristalización por fusión) separates components based on crystallization temperature from the melt. Compared with distillation, it reduces thermal stress, lowers energy demand for high-purity cuts, and achieves excellent color and inhibitor control.
Hybrid trains combine preliminary stripping/dehydration with multi-stage melt crystallizers and wash columns, achieving competitive OPEX and significantly improved safety margins.
4.2 Melt Crystallization
Process principle: selectively crystallize acrylic acid from a stabilized melt near its melting point, reject impurities to mother liquor, then wash and remelt to obtain high-purity product.
Representative steps:
- Feed conditioning: stabilize crude acrylic acid with inhibitors; dehydrate and filter fines.
- Nucleation and growth: cool the melt on heat-transfer surfaces in layer or suspension crystallizers to form controlled crystals.
- Sweating: gently warm to expel trapped mother liquor and concentrate impurities away from the crystal phase.
- Washing: use a wash column to displace residual impurities with a thin melt layer counter-flow, enhancing purity without solvents.
- Remelting and polishing: melt crystals under inert gas, fine-filter, and adjust inhibitor content to specification, yielding ice crystallized acrylic acid.
Technical Benefits
- Purity at or above 99.5% with low color and low aldehyde content
- Energy efficiency (lower reboiler loads vs. deep-vacuum distillation)
- Inherently safer operation (lower polymerization propensity)
- Shorter hot-residence time and modular scale-up
Operational Challenges
- Managing supersaturation and crystal habit
- Controlling inhibitor distribution and oxygen traces
- Preventing fouling on heat surfaces
- Ensuring wash-column hydraulics for uniform purification
Global adoption: Broadly deployed in Europe and Asia in new builds and retrofits to reduce energy intensity and improve product stability for long-haul shipments. Technology providers offer standardized packages; design practices reference Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook and the VDI Heat Atlas for crystallization thermodynamics and heat transfer.
5. Trends and Challenges
5.1 Emerging Trends
Sustainability
Lower-carbon electricity/steam, heat integration, and solvent-free purification; exploration of bio-routes from glycerol or lactic platforms.
Regional Expansions
Asia-Pacific continues to add capacity alongside downstream SAP and acrylates integration.
Regulatory Tightening
Stricter worker exposure limits, transport temperature controls, and inhibitor specifications impact storage and logistics.
5.2 Key Challenges
Feedstock Volatility
Propylene price swings and PDH reliability drive margin uncertainty, affecting upstream cost structures.
Safety and Environment
Polymerization hazards, inhibitor stability, and wastewater minimization demand continuous investment in process safety systems.
Technology Gaps
Optimizing crystallizer fouling control, developing digital twins for dynamic operation, and designing flexible trains for variable crude quality.